Weight regulation is complex and influenced by biology, environment, behavior, and health status. Plateaus do not mean failure or a broken metabolism.
Let's look at the physiology-based explanations for when the scale won't budge.
1. Energy balance still matters (but it’s not the whole story)
Weight change requires an energy imbalance, but many factors influence how the body responds, including:
- Hormonal regulation
- Sleep
- Stress
- Medication effects
- Adaptive metabolic responses
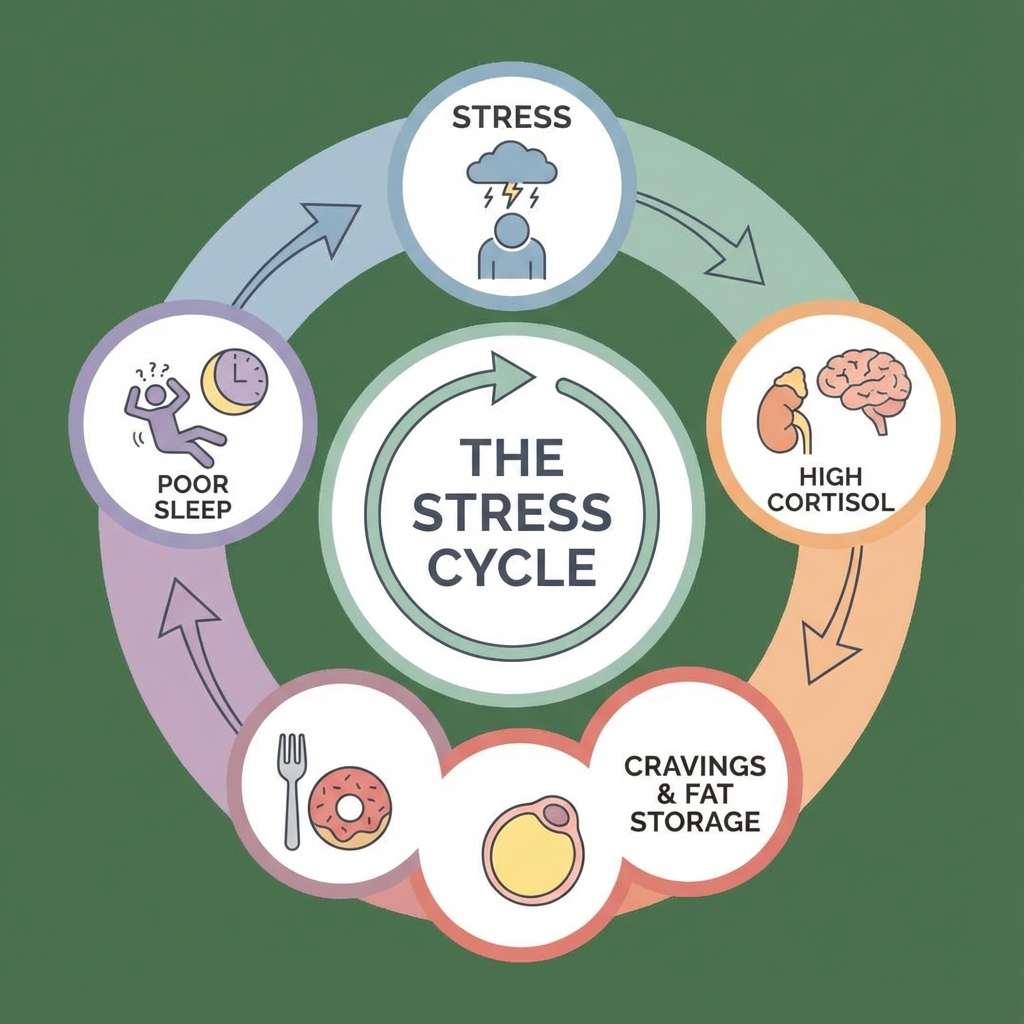
2. Sleep and stress play a major role
Chronic sleep deprivation is associated with:
- Increased hunger hormones (ghrelin)
- Reduced satiety signaling (leptin)
- Altered insulin sensitivity
High stress can increase cortisol, which may influence appetite, food choices, and fat distribution.
3. The gut microbiome: promising but not deterministic
Research suggests associations between gut microbiota patterns and metabolism, but:
- The microbiome does not override calories
- It does not independently cause weight gain
- Individual prediction is currently limited
✔️ Perspective: Microbiome-supportive habits (fiber, diversity, regular meals) are
beneficial for overall health, not guaranteed weight loss hacks.
4. Medical and medication factors
Conditions that may affect weight loss include:
- Thyroid disorders
- PCOS
- Insulin resistance
- Perimenopause/menopause
- Certain medications (antidepressants, steroids, beta blockers)
These require medical evaluation, not dietary extremes.
Sustainable weight management focuses on:
- Adequate protein intake
- Balanced carbohydrate intake
- Sufficient sleep
- Resistance training
- Stress reduction
- Consistency over perfection
Evidence-based references
- Hall et al., Lancet, 2019
- NIH Obesity Research
- Spiegel et al., Annals of Internal Medicine, 2004
- Turnbaugh et al., Nature, 2006
- Jensen et al., AHA/ACC/TOS Guidelines, 2014
Disclaimer: This content is for educational purposes and does not replace
individualized medical care. Nutrition and digestive health recommendations should be personalized
and discussed with a qualified healthcare provider.

